Wilfred Mijnhardt has a dilemma. Europe is home to some of the world’s oldest and most prestigious business educational institutions, and it has been at the forefront of significantly of the world wide innovation in training and research on sustainability.
But when he analyses institutions’ effectiveness centered on their position in over-all rankings, permit on your own their tutorial research output, he finds a important mismatch with those executing most to foster liable business schooling.
Mijnhardt, plan director at Rotterdam College of Administration at Erasmus College, is a person of a expanding range of professionals discovering strategies to better seize these types of trends. It is also a concern on which the FT is reflecting and canvassing sights in conjunction with tutorial and sustainability teams. Notably, Mijnhardt has mapped the inbound links involving the business schools’ research output and the UN’s sustainable advancement aims (SDGs).
“Business educational institutions are lagging driving [other disciplines],” he says. “They think that if they make a handful of publications that rely for rankings and accreditation uses, they are executing research. But this environment is significantly even bigger than that and tutorial tradition is so significantly a lot more.”
Mijnhardt analyzed content articles on SDGs created by business school workers considering that 2015 that were printed in the FT50 record of influential journals. He uncovered that the major establishments are ever more centered on the area, with solid output in Europe from educational institutions at the universities of Glasgow, Leeds and St Gallen, for instance.
But there are massive gaps, with weather transform-connected subject areas explored significantly a lot less in these content articles than themes these types of as poverty reduction and innovation. Some of the content articles with the finest SDG relevance and impression are printed in a lot more obscure and a lot less very well-regarded journals.
Mijnhardt indicates business educational institutions have moved a lot more slowly and gradually than other tutorial departments to work on a lot more interdisciplinary, collaborative and socially relevant themes. Just one explanation is they are a lot less reliant on — and accountable to — exterior research funders which are ever more centered on the priorities of the SDGs. As a substitute, their research tends to be indirectly subsidised by higher tuition charges or donations.
Jerry Davis, affiliate dean for business and impression at Ross College of Organization at the College of Michigan, is a lot more nuanced. “Business educational institutions ironically are a person of the very last preserves the place you are absolutely free to observe your thoughts the place it goes, due to the fact you are not reliant on government or company funding,” he says. “We have likely a lot more tutorial freedom to uncover matters.”
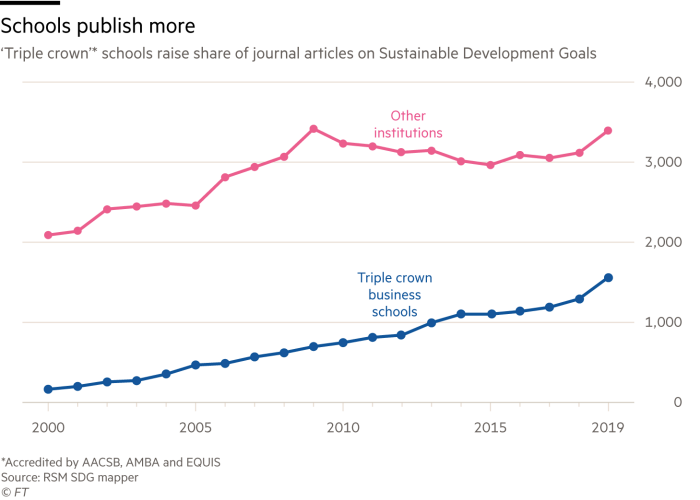
Educational institutions with the prestigious ‘Triple crown’ of accreditation from the AACSB, AMBA and EQUIS are publishing a lot more content articles connected to UN sustainable advancement aims in the FT50 record of influential tutorial journals utilised in business schooling rankings
Still in apply, as a founding member of Responsible Investigation for Organization & Administration (RRBM), a network of academics pushing for “credible and handy research”, he says a lot more requirements to be done to reorient his peers’ actions to assignments and publications that offer you increased societal impression.
Just one critique of current business school rankings, like the FT’s, is that their calculations do not emphasis so significantly on these subject areas. As a substitute, they draw on details factors these types of as salaries that do not replicate — and might even likely undermine — expanding demand by learners, college and businesses for a increased emphasis on these types of social function, like in their tutorial output.
But there is a a lot more elementary concern for those keen to carry about transform: the lack of consensus on strategies to meaningfully assess these types of actions. Other assessments centered on the SDGs depend heavily on subjective, qualitative judgments by learners and college. They are limited by reference to their individual ordeals and establishments, without the need of an exterior benchmark.
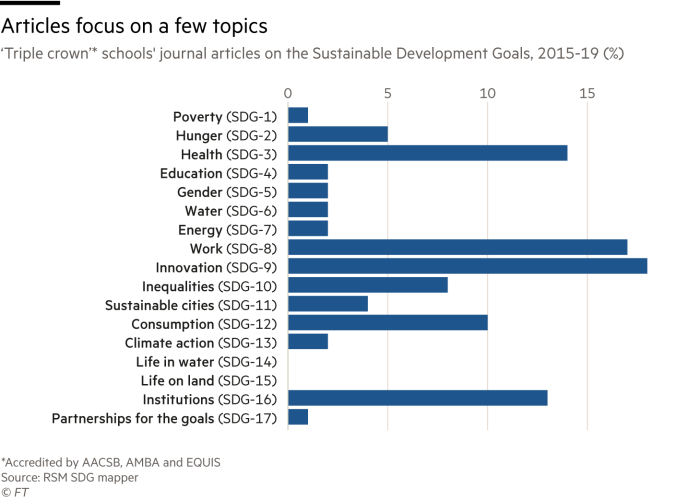
Organization school academics have a tendency to emphasis heavily on particular SDGs, most notably well being, innovation, work, intake and establishments, while topics these types of as the earth, poverty, schooling and gender get somewhat tiny awareness
It is in particular complicated to consider the impression of “environmental, social and governance” factors in classroom training or alumni professions. Even in tutorial research, very long scrutinised by way of “bibliometrics” discovering the details about printed research, there is tiny agreement on which actions to use.
Focusing on the material of content articles that refer to the SDGs delivers a proxy on the extent of activity about these difficulties. But it presents only a crude yardstick for the originality, worth or applicability of the fundamental research.
Specialists these types of as Amanda Goodall, affiliate professor at The Organization College, Town, College of London (previously Cass), advocate growing the assortment of publications that are taken into account outside of those in the commonly recognised and prestigious FT50, to incorporate a lot more interdisciplinary and professional journals. That would enable for a wider variety of themes but could also dilute the perceived tutorial high quality.
Working with citations by other academics of content articles would aid counter criticism by adding a peer assessment of the high quality of any publication. But it does not give an indication of the impression outside of university walls: the extent to which research is read, shared and carried out by companies, governments and other organisations. References to content articles on social media supply some exterior validation of interest but also a higher diploma of “noise”. A better technique may possibly be take into account references to tutorial research in the media, professional blogs and plan papers.
These are some of the difficulties on which the FT, RRBM, the UN’s Concepts of Responsible Administration network and some others, like the Globally Responsible Leadership Initiative of business educational institutions, are looking for sights.
Irrespective of the difficulties, Prof Davis is optimistic about academia’s ability to acquire choice measurements, in aspect due to the fact of new interest in societal impression within schooling and outside of. “Millennials have a quite solid feeling of social justice and the impact of the work they do. I’m really enthused by the coming generations,” he says.
You should share your sights on how to better measure tutorial research at ft.com/ft50






More Stories
How to Protect Your Tan While You Vacation?
Choosing Reliable and Trustworthy Auto Shop in Brisbane
How Technology Has Changed The Face Of Dentistry